Ondat Cluster Topologies
Overview
Ondat makes it possible for cluster administrators to design and implement different cluster topologies, depending on types of workloads, use cases, priorities and needs. The topology approaches recommended below are idealised representations of possible Ondat clusters and can be mixed, modified and changed at execution time.
Ondat performs file Input/Output (I/O) operations over the network, which is how the platform ensures that data is always available throughout your cluster. This also affords cluster administrators certain possibilities of organising their clusters in ways explained below.
Hyper-converged Cluster Topology
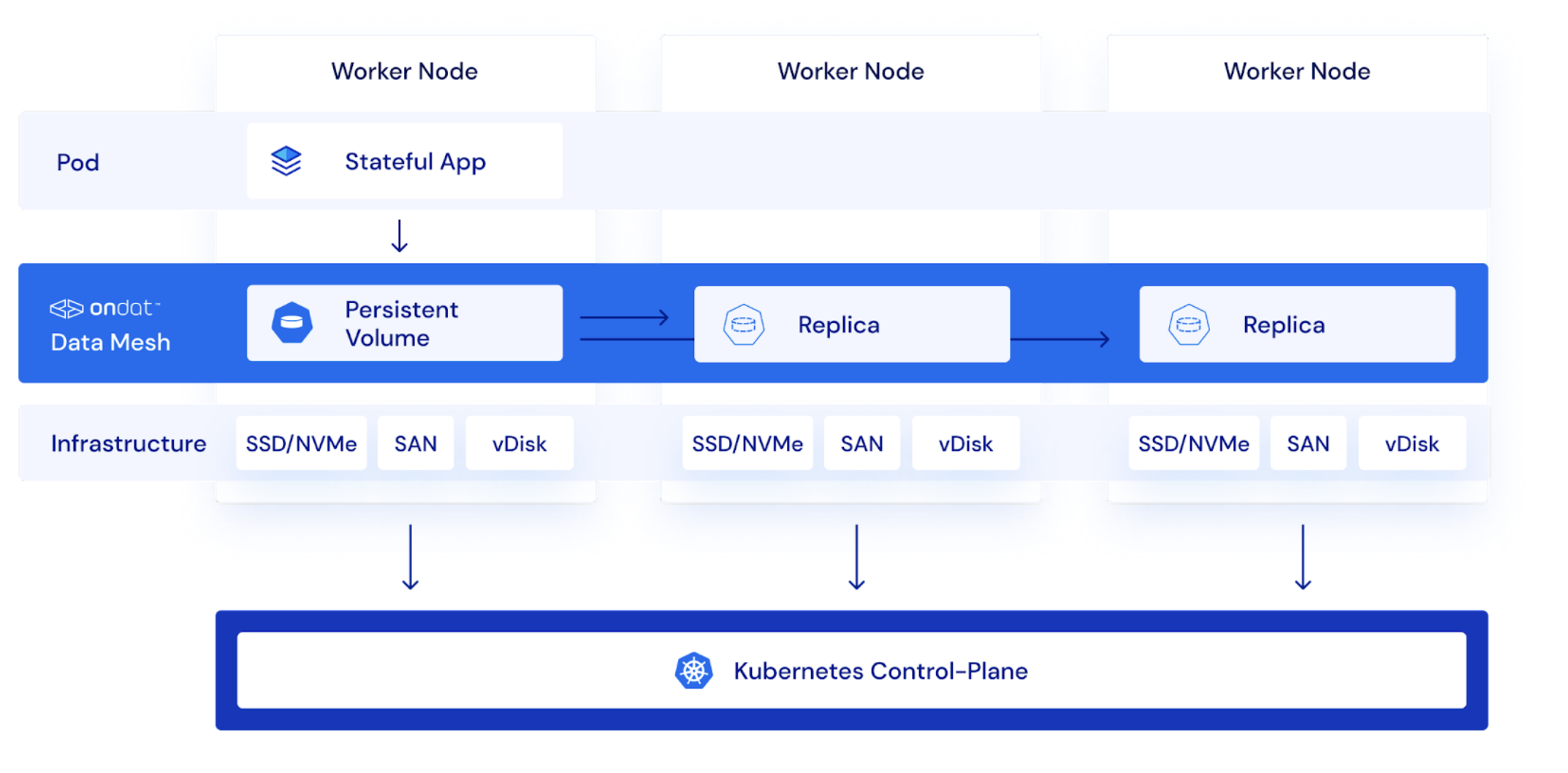
- The hyper-converged cluster topology model leverages the available block storage attached to all the worker nodes in a Kubernetes cluster, creating a single storage pool that stores and present data for stateful workloads deployed and running.
- This cluster topology gives the best flexibility to Ondat and Kubernetes schedulers, and provides maximum choice for optimal pod placement when pods are being assigned to nodes in a cluster.
- No matter how or where workloads are deployed on worker nodes, Ondat will ensure that the data from workloads is stored, persistent and always accessible.
- New Ondat deployments will place workloads locally where possible using this hyper-converged cluster topology out of the box.
Centralised Cluster Topology
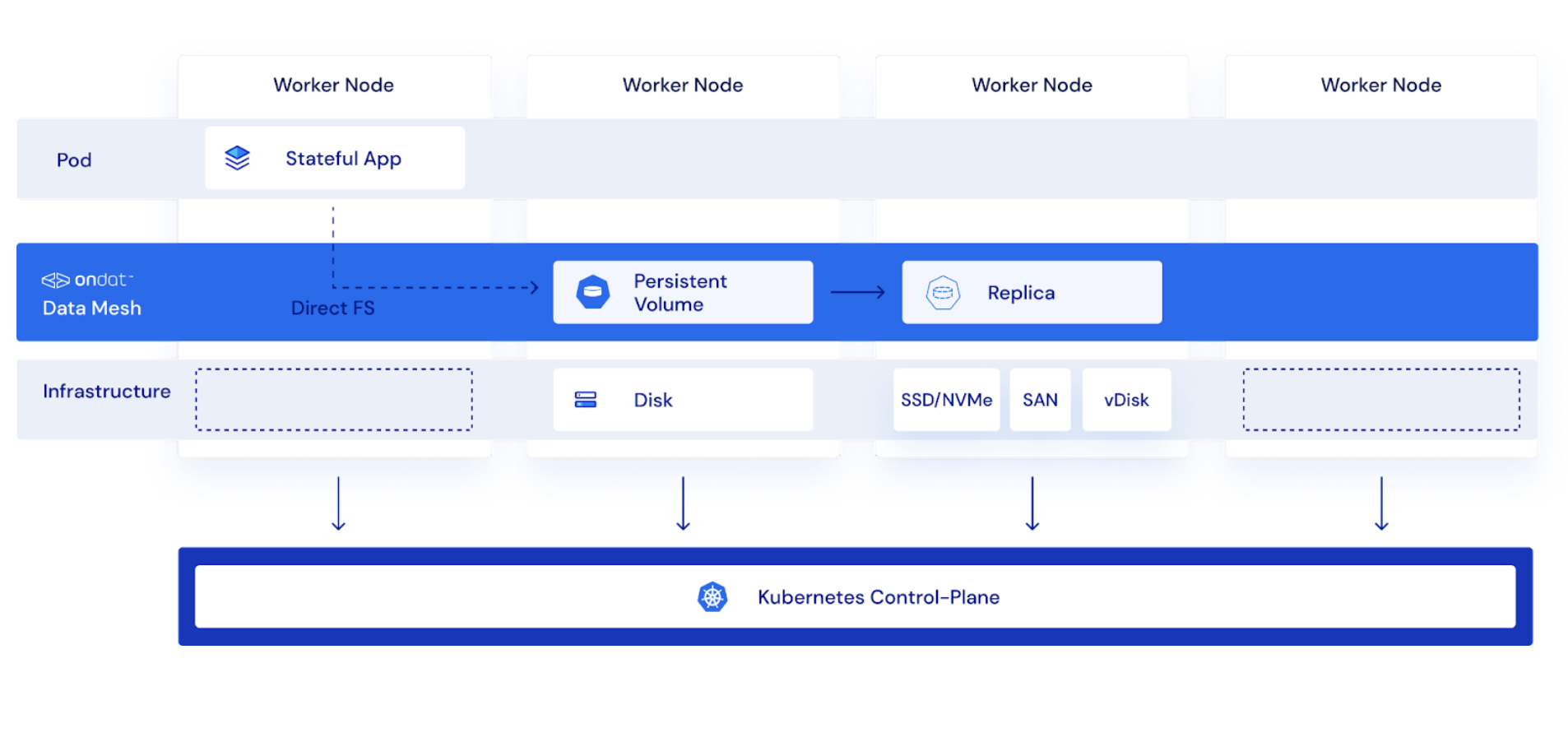
- The centralised cluster topology model leverages the available block storage attached to only a subset of worker nodes (creating a dedicated, storage-optimised node pool) in a Kubernetes cluster, whilst the rest of the worker nodes are dedicated to running general and compute-intensive workloads,
- Deployed workloads in centralised cluster that require data persistency will access a dedicated storage pool that is located on the declared subset of worker nodes.
- This cluster topology can be beneficial if, for example, cluster administers want to take advantage and effectively utilise high performance-optimised hardware components of a particular set of worker nodes for different types of workloads being deployed.
- The cluster topology can also aid in avoiding downtime issues that can arise from unaccounted resource/capacity planning and allocation for workloads, since storage-optimised nodes and compute-optimised workloads are compartmentalised.
- In addition, another suitable use case for this topology is for elastic worker node fleets with burst-able workloads. A fleet can be quickly expanded with new worker nodes for compute-intensive workloads on demand, whilst maintaining a centralised data storage pool that is not impacted by rapid auto cluster scaling.
- To configure this cluster topology for a new Ondat deployment, cluster administrators would need to apply an Ondat node label called
storageos.com/computeonlyto nodes, which would inform Ondat that it should not use the nodes to join a storage pool.- Review the Centralised Cluster Topology operations page for more information on how to use this topology model for your clusters.